The basic structure of MONAS
The basic structure of MONAS K-series is shown in the picture below. The optimal specifications can be selected with various options according to the application, such as the properties, use, and flow rate of the transfer liquid, etc.
Please click on a part or name of the pump to see a detailed description of that part.

Please click the mouse on the corresponding part. You can see detailed explanation.
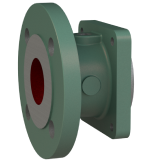
Discharge Flange
- The flange standard may be various according to requirements of KS, ISO, ANSI etc.
- It serves as a suction flange, in case of reverse rotation.
End Stud
Made of the same material as the pump casing.
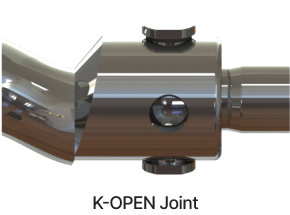
Universal Joint
The progressive cavity pump rotor has an eccentric motion that deviates from the centerline of the drive shaft, so we have to connect a coupling rod and two universal joints between rotor and drive shaft. MONAS′ Joint is made of PIN JOINT, which is durable, simple, and in perfect sealing structure. (patent) In the case of Sanitary, it is made of OPEN TYPE for easy cleaning.

Suction Flange
- The flange standard may be various according to requirements of KS, ISO, ANSI etc.
- In case of reverse rotation, this flange serves as a discharge flange.
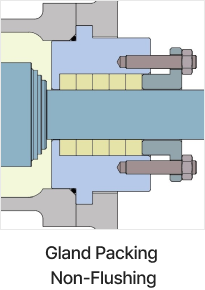
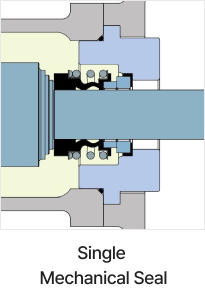
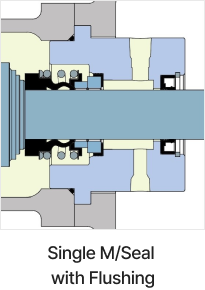
Shaft Seal
Shaft sealing device prevents leakage of transfer fluid through the drive shaft penetration part. An appropriate shaft sealing method can be selected. Gland packing has flushing type and non-flushing type. Mechanical seals have a variety of specifications such as single m/seals, flushing types, and double seals etc.
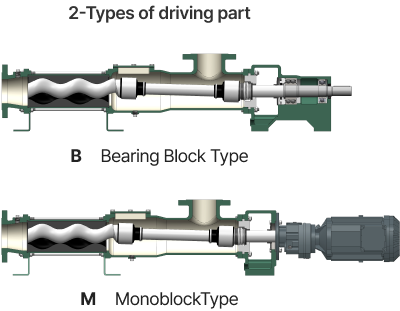
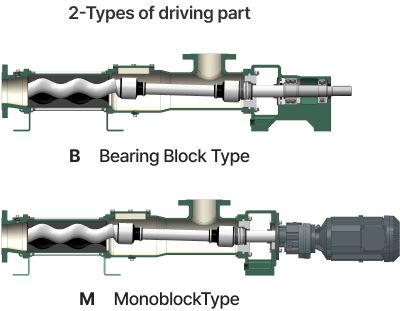
Bearing Block
As the drive shaft supported by the bearing block is connected to the seperate driver through flexible coupling, driver can be freely selected.

Drive Shaft
-
The drive shaft of bearing block is manufactured in a split type and consists of a drive shaft supported by bearings and a connecting shaft to which the sealing device is assembled. The drive shaft is inserted into the connecting shaft and assembled and secured with pin.

- In case of the mono block type, instead of the drive shaft in bearing block type, the shaft of the drive reducer is directly coupled to the connecting shaft.
Connecting Shaft
-
In the case of the bearing block type, a connecting shaft is coupled to the drive shaft, and in the case of the monoblock type, it is coupled to the shaft of the drive reducer.

Mono Block Bracket
The reducer is directly assembled to the mono block bracket, so it is of compact and simple structure. However, the pump connecting shaft cannot stand alone if the reducer is seperated, and only specific reducers can be assembled.

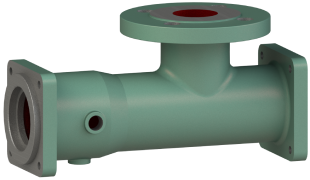
Pump Casing
Made of a material suitable for the transfer liquid.
Pump Casing Material
| Cast Iron | Gray Cast Iron |
|---|---|
| Stainless | STS304, 316 |
| Special | Titanium, Hastelloy-C |
Coupling Rod
Made of a material suitable for the transfer liquid, and if necessary, screws for suspended solids or wings for preventing precipitates may be attached.

Stator
Female screw made of elastomeric material with long-oval cross-section
The stator is made by molding special synthetic rubber in a precision core mold with a high pressure injection molding machine. Depending on the application, various rubber materials are available. For special medium, teflon stators are available.

Material of Stator
| Abrasion resistant | NBR |
|---|---|
| Corrosion resistant | Hypelon, EPDM, Viton |
| Special-corrosion resistant | Teflon(PTFE) |
Rotor
Male screw made of metal, with perfect-circular cross-section
This is precisely manufactured with various materials and specifications according to the applications, and is specially heat-treated or plated with hard chrome of a sufficient thickness for abrasion resistant.

Material of Rotor
| Abrasion resistant | STD11 + Q/T |
|---|---|
| Corrosion resistant | STS304, 304HCr STS316, 316HCr |
| Special-corrosion resistant | Titanium, Hastelloy-C, etc. |
